For this physical science activity students draw force diagrams and identify the types and directions of forces illustrated in the printable. The dancer is leaning on the table at an angle while stretching.

Force Diagrams With Component Forces Youtube
Label the force vectors and use equality marks on the vectors.

. David goes through a bunch of examples and shows how to find the directions of forces exerted on an object. A box is pushed up an incline with friction which makes an angle of 20 with the horizontal. To better understand how to draw free-body diagrams using the 3 steps lets go through several examples.
Draw a force diagram for the water-skier. Draw a force diagram for the water-skier. Draw a force diagram for the person.
Draw a force diagram for the table. Also use congruency marks to indicate which vectors are equal in magnitude. Note that the pull on the sled is at an angle.
A A soccer player using his foot applies a force to the ball. In this case place a squiggly line through the original vector to show that it is no longer in playit has been replaced by its x and y -components. Include the weight of the sled the normal force and the force on the sled due to the girls pull.
Note that the pull on the sled is at an angle. Label the force vectors and use equality marks on the vectors. Draw a force diagram for the sled and kids moving at constant velocity.
Label the force vectors and use equality marks on the vectors. B A person skydiving has a force of gravity on them from the earth. Draw a free body digram and label 2 arrows indicating the force described and a arrow for thereaction force.
Draw a force diagram for the sled and kids. Lets draw the free-body diagram of the box. Label the force vectors and use equality marks on.
Draw a force diagram for the water-skier. The first step is to sketch what is happening. Also use congruency marks to indicate which vectors are equal in magnitude.
Label the force vectors and use equality marks on the vectors. C A bow applies a force to an arrow right right before it is released. Note that the pull on the sled is at an angle and is traveling at a constant speed.
A ball at the top of a parabolic trajectory af 1 1. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics. Note that the pull on the sled is at an angle.
A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. The direction of the arrow shows the direction that the force is acting. Draw a free body diagram to show the forces acting in each example.
Draw a force diagram for the sled and kids. Draw a force diagram for the sled and kids. Draw a properly scaled and labeled Force Diagram for each object of interest 2.
The sled and kids are are not accelerating Velocity vector Right arrow Force diagram Simplified force diagram Fnet ma m0 0 N Horizontal force equations. Equilibrium Attained Net Force 0 Newtons Draw a free body diagram with a 10 N force and a 25. Off to the side of your Force Diagram use the tip-to-tail method to determine the net force on each object 3.
Draw a force diagram for the sled and kids. Label the force vectors. Forces and Force Diagrams.
Friction Ftension Vertical force equations. Sketch all the forces acting upon the object making the length of each vector represent the magnitude of the force. Label the force vectors and use equality marks on the vectors.
Draw a force diagram for the sled and kids. Label the force vectors and use equality marks on. Draw a force diagram for the sled and kids.
How to draw force diagrams when you need to break non-vertical or non-horizontal forces into X- and Y-components. The sled with the boy has a weight of 400 Newtons and the girl pulls with a force of 100 N at an angle of thirty degrees above the horizontal. B You push a sled carrying your c A person hangs from a Draw the forces acting on the little brother across the snow.
Examples of drawing free-body diagrams. Calculate the normal force of the ice on the sled. Object making the length of each vector represent the magnitude of the force.
Label the force vectors and use equality marks on the vectors. Note that the pull on the sled is at an angle. A A plant sits on a bookshelf.
Convert the free-body diagram into a more detailed diagram showing the x and y-components of a given force this is often helpful when solving a problem using Newtons first or second law. The size of the arrow in a free-body diagram reflects the magnitude of the force. The sled and kids note that the A ball rising in a parabolic pull on the sled is at an angle.

Solved M Dog M Sled 30o A Sled Is Pulled Along A Surface Chegg Com

Draw A Free Body Diagram To Represent The Following Situation Make Sure To Label All Forces And Give Their Magnitudes A Child On A Sled Is Sliding Down A Snow Covered Hill The Child
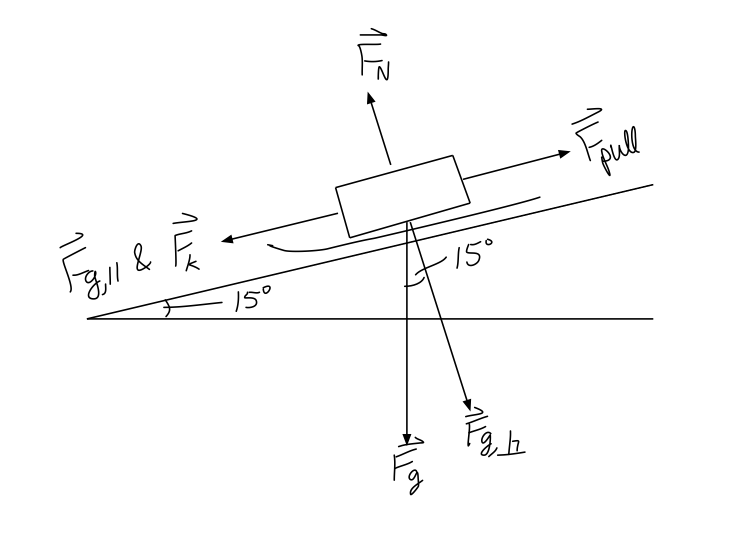
A Man Pulls His Child In A Sled At A Constant Velocity The Child And Sled Have A Combined Mass Of 60 Kg The Force Applied On The Handle Is 200n At
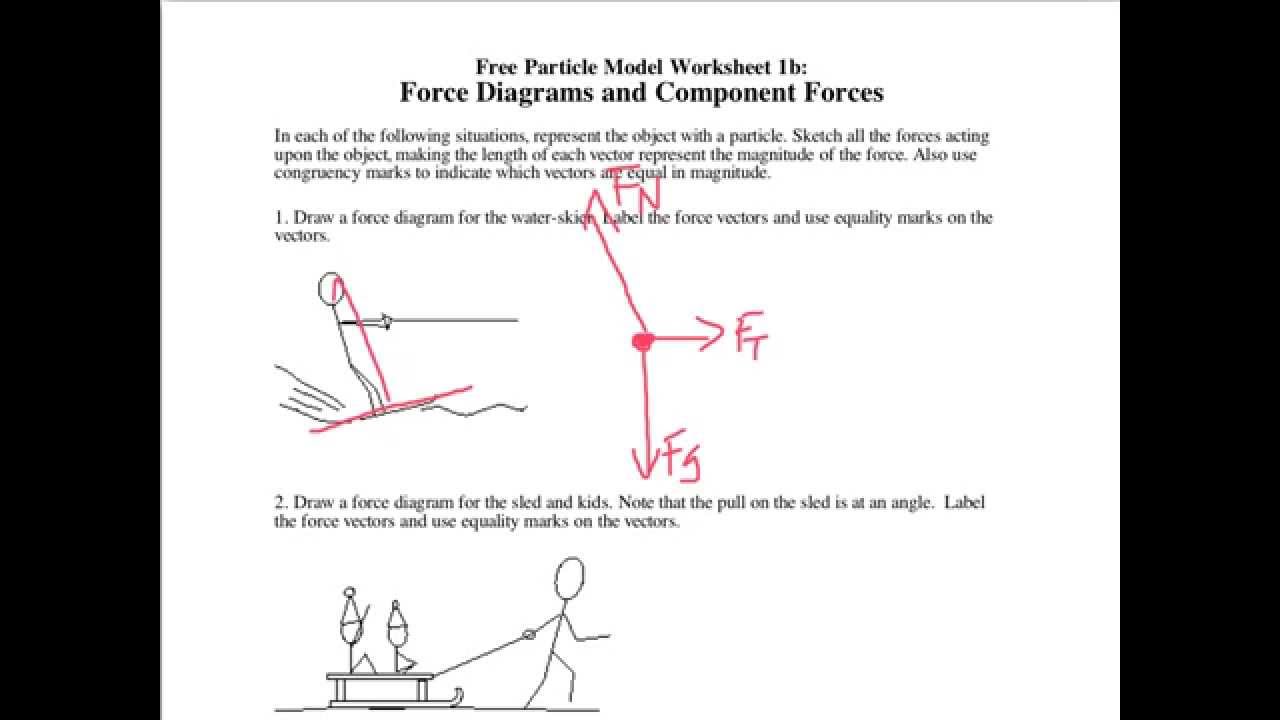
Drawing Force Diagrams And Finding The Resultant Net Force Youtube

Solved The Sled In Figure 4 2 Is Stuck In The Snow A Child Pulls On The Rope Solutioninn
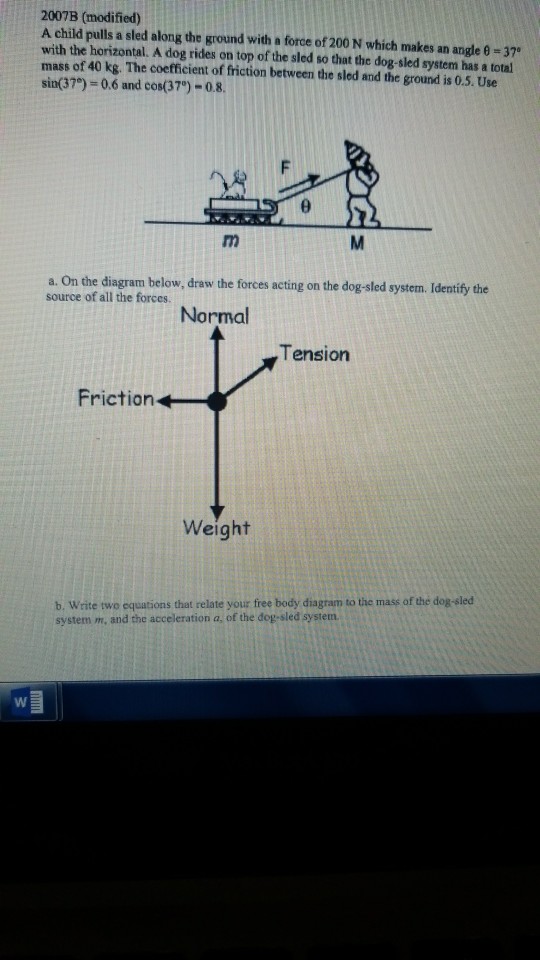
Solved 2007b Modified A Child Pulls A Sled Along The Chegg Com
Sledding Force Diagrams And N2

01 Force Diagrams Pdf Name Sarah Boothe Date Pd Free Particle Model Worksheet Force Diagrams And Component Forces In Each Of The Following Course Hero
0 komentar
Posting Komentar